- +86-0533-2185556
- WhatsApp: +86 15965530500
- admin@hangyubiotech.com
Your Location:Home >Products >small-molecule inhibitor >25189-55-3
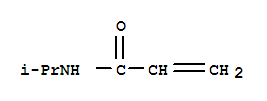
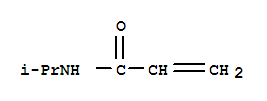
pd_meltingpoint:96 °C(lit.)
Appearance:White to Off-White
Purity:99%
|
Definition |
ChEBI: An acrylic macromolecule, arising from poymerisation of N-isopropylamide. |
|
General Description |
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) is a temperature-responsive polymer used in biomedical research applications. PNIPAM undergoes a reversible, lower critical solution temperature (LCST) phase transition when heated above 32 °C, transitioning from a soluble to an insoluble material. PNIPAM is also frequently crosslinked to yield hydrogels with reversible, thermal shrinking and swelling. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) is also readily functionalized and has been used as the hydrophilic block in the synthesis of thermoresponsive, amphiphilic block copolymers. Due to the similarity in temperature between the LCST of PNIPAM and the temperature of the human body, PNIPAM materials have been frequently utilized in tissue engineering and controlled drug delivery research applications. |
InChI:InChI=1/C6H11NO/c1-3-5-7-6(8)4-2/h4H,2-3,5H2,1H3,(H,7,8)
CAS:112163-33-4
CAS:112-84-5
CAS:10361-93-0
CAS:45235-48-1